The Optimizer and RUNSTATS are important parts of DB2. They help in keeping track of statistics about your tables. The Optimizer uses these statistics to make smart decisions when processing your queries. It takes into account factors such as the number of rows, indexes, index cardinality, and the number of pages used. These statistics are stored in catalog tables and are used by the Optimizer.
Table of contents
DB2: Optimizer Vs. RUNSTATS
Optimizer
RUNSTATS
Automated
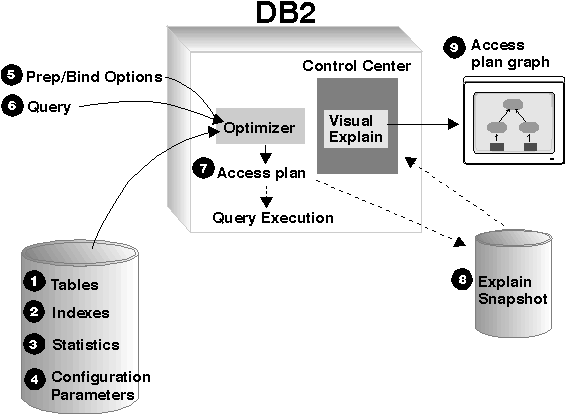
- In the above flow, it is clearly stated that Optimizer has access to Statistics, Bind Options, and SQL Query.
- The Optimizer prepares an access-plan to the SQL query. From the snapshot, the Access plan goes to the Visual Explain, which is a tool, you can view the execution in visual mode.
- The collection of statistics is an automated process. So from the developer side, it is nothing to do.
Manual
The developer can use the RUNSTATS command on the Table and indexes to update catalog tables (This you need during building SQL query for the first time).
The purpose is to get insights about the Queries (This is useful to issue explain plan command after executing RUNSTATS). So, the developer can fix the query if optimization is needed.
Example:
RUNSTATS ON TABLE employee AND DETAILED INDEXES ALL;RUNSTATS collects a wealth of information about; Table, and the indexes on the table, such as index “height,” number-of-pages at the leaf level, and more. Gathering this index-related information is controlled using the indexes clause.







You must be logged in to post a comment.