Here are to methods add rows to a table in SQL. These include adding directly and with Select.
Table of contents
Insert Directly
Example-1: SQL Query
INSERT INTO my_table (name, id, salary)
VALUES ('Srinimf', 1001, 150000);When inserting data into a table, if the values are in sequence with the columns, you don’t need to specify the column names. However, if the values don’t match the column sequence, you must provide the column names. The columns for which you haven’t inserted any values will have their default values, such as NULL. All NOT NULL columns you must supply values.
Audio explanation
Insert with select
Here, from the select statement, you’ll get the data, and the same you can insert into new table.
- INSERT INTO
- SELECT
Example-2: SQL Query
Ensure that you should be created NEW_TABLE with the same columns before you copy the data.
INSERT INTO NEW_TABLE ( name, id, salary)
SELECT name, id, salary
from MY_TABLE
WHERE id = 1001;After executing the SQL query, the data from the MY_TABLE will be inserted into the NEW_TABLE. You can then view the data in the NEW_TABLE. This example is designed for use with DB2.
The following screen shows my testing of this SQL query.
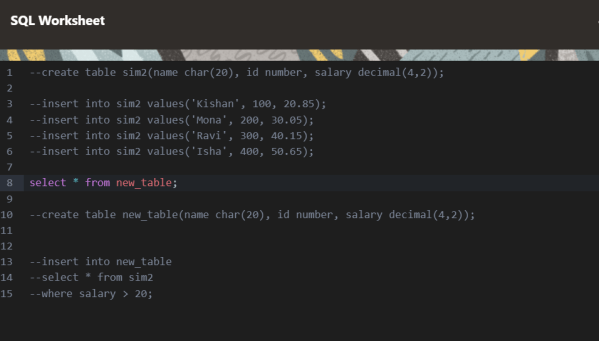
Conclusion
The given SQL queries demonstrate how to insert values into a table and select values from another table in a single query. These examples illustrate the use of INSERT INTO and SELECT statements to accomplish this task efficiently. It’s important to ensure that the new table has the same columns before copying the data, and to handle any mismatches between the values and column sequence appropriately. Overall, these methods provide a streamlined approach to data manipulation in SQL.







You must be logged in to post a comment.