Here are details explained ORC vs Parquet vs Avro performance.
Table of contents
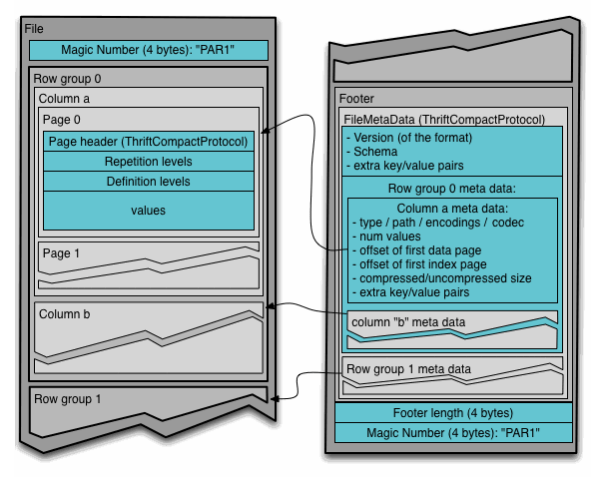
Parquet File Format
Row-columnar Parquet refers to the Parquet file format, which is designed for efficient data storage and retrieval. Parquet is a columnar storage format, meaning it stores data by columns rather than by rows. Here’s a breakdown of the terms:
- Row storage: Data is stored row-by-row. Each row in a dataset is stored sequentially. This format is best suited for cases where you frequently access the entire row of a dataset.
- Columnar storage (Parquet): Instead of storing rows, data is stored column-by-column. This allows for more efficient reads. It is particularly useful when you need only specific columns. This reduces the I/O and speeds up queries. It is well-suited for analytical queries where you often perform operations on a subset of columns (like aggregations).
Key Features of Parquet:
- Efficient storage: Columnar storage reduces the amount of data read from disk when querying only a few columns.
- Compression: Since the data in each column is often of the same type, Parquet allows efficient compression, reducing storage requirements.
- Schema evolution: Parquet files support schema evolution, which makes it easier to add new columns over time without having to rewrite the whole dataset.
ORC File Format
ORC (Optimized Row Columnar) is a highly optimized columnar storage format. It is used primarily in big data processing frameworks such as Apache Hive and Apache Spark. It was designed to efficiently store and retrieve large datasets in a Hadoop ecosystem.
Key Features of ORC Files:
- Columnar Format: Like Parquet, ORC stores data column by column. This makes it very efficient for reading subsets of columns in large datasets. This is especially true in analytical workloads where you’re often querying specific columns rather than entire rows.
- Efficient Compression: ORC supports various compression algorithms like ZLIB, SNAPPY, and LZO, allowing for highly efficient compression. Because data is stored column by column, similar data types can be compressed more effectively.
- Splitting and Parallel Processing: ORC files are split into “stripes,” and each stripe contains multiple rows from the dataset. This allows big data processing engines like Hive and Spark to read and process large datasets in parallel, improving performance.
- Indexing:
- ORC files include lightweight indexes for each column. These include the minimum and maximum values. This makes it easier to skip over non-relevant data when querying.
- Each stripe includes an index, helping the query engine locate specific sections of the data without scanning the entire file.
- Predicate Pushdown: ORC files support predicate pushdown, meaning that filters on specific columns (e.g.,
WHERE column_name > 100) can be applied at the storage level. This avoids scanning unnecessary rows and speeds up queries. - Schema Evolution: ORC supports schema evolution. This means you can add new columns to the data schema over time. You can do this without breaking compatibility with old files.
Structure of ORC Files:
An ORC file is composed of three main sections:
- Stripes: Each stripe contains a section of the data. Stripes include data for each column in the dataset.
- Footer: The footer contains metadata, such as the schema and statistics about the file.
- Postscript: Contains information about the compression used in the file and the length of the footer.
Benefits of ORC:
- Reduced File Size: ORC provides better compression than row-based formats like CSV or JSON. It also offers better compression than some other columnar formats. This makes it ideal for storing large datasets.
- Improved Performance: ORC’s optimized columnar format and indexing help improve query performance. They reduce the amount of data that needs to be read.
- Efficient Aggregations: Since ORC stores data by column and keeps statistics, operations like aggregations (sum, average, etc.) are much faster.
- Compatibility: ORC is widely used in the Hadoop ecosystem. It is compatible with many tools such as Apache Hive, Apache Spark, and Apache Pig.
When to Use ORC:
- Big Data Analytics: ORC is ideal for workloads that involve large-scale analytical queries. You often work with a few columns rather than entire rows.
- Hive and Hadoop Workloads: ORC was initially developed for Apache Hive. This makes it highly suitable for Hive and Hadoop-based data lakes.
- Efficient Storage: When you need to store large datasets efficiently, particularly when disk space or network I/O is a concern.

AVRO File Format
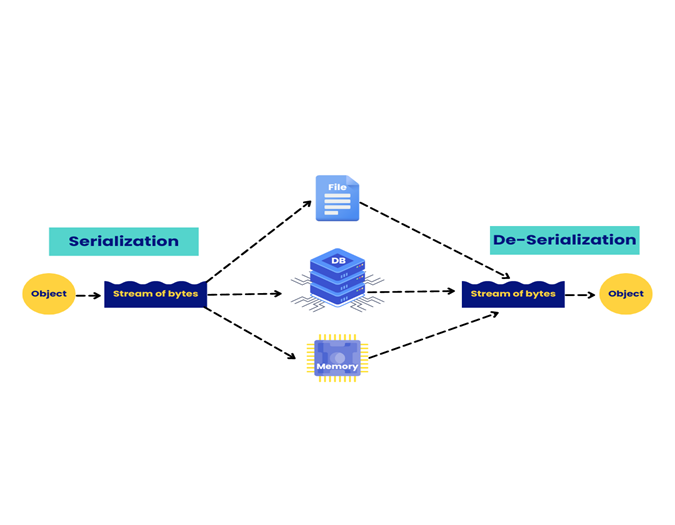
An AVRO file is a data serialization format developed within the Hadoop ecosystem, designed to store structured data efficiently. It is widely used in big data and streaming applications, especially when integrating various systems.
Key Features of AVRO:
- Row-Oriented Storage: Unlike Parquet and ORC, which are columnar formats, Avro stores data in a row-oriented fashion. This makes it a good choice for write-heavy workloads. It is also useful when dealing with streaming data where entire records need to be accessed.
- Schema-Based: AVRO files are tightly coupled with schemas. The schema is stored as part of the file and is in JSON format, which describes the structure of the data (fields, data types, etc.). This makes Avro very suitable for systems where data evolves over time (e.g., adding new fields), as the schema helps in maintaining compatibility.
- Compact and Efficient: Data in an AVRO file is stored in a binary format. This ensures compact file sizes. It also allows efficient serialization and deserialization. The schema is in JSON, but the data is stored in binary format for optimal storage and performance.
- Cross-Language Support: Since the schema is stored alongside the data, AVRO files are language-agnostic, meaning they can be written and read in multiple programming languages (Java, Python, C++, etc.). This is important for interoperability between different systems.
- Compression: AVRO supports block-level compression using algorithms like Snappy and Deflate, which reduces file size without affecting performance significantly.
- Schema Evolution: One of the major advantages of AVRO is that it supports schema evolution. Over time, as the structure of your data changes (e.g., adding, removing, or modifying fields), Avro allows these changes as long as the schema maintains compatibility with previous versions. This makes it suitable for long-lived data systems where schema changes are common.
- Efficient Data Streaming: AVRO is row-based and includes the schema with each file. It is particularly useful for data streaming systems. One example is Kafka. In these systems, messages need to be serialized and deserialized efficiently.
Structure of an AVRO File:
An AVRO file consists of two main parts:
- Schema: This part is stored in JSON format and describes the data structure.
- Data: The actual data is stored in a binary format to optimize storage and performance.
Each Avro file contains a header that includes the schema and blocks of serialized data. The schema is stored only once in the file, making AVRO both space-efficient and easy to read/write across systems.
Use Cases for AVRO:
- Data Interchange: AVRO is used in scenarios where data needs to be exchanged between different systems. These systems may use different programming languages. The built-in schema helps ensure compatibility.
- Streaming Platforms: In distributed streaming platforms like Apache Kafka, AVRO is commonly used to serialize data. It ensures compact storage and schema evolution. This is vital for real-time data processing.
- Hadoop: AVRO is well-suited for use in Hadoop and related systems. This is because of its compact binary format. It also supports distributed processing. It can be used as an input/output format in MapReduce and works well with Apache Hive.
- API Communication: AVRO can also be used in web service communications where serialized data needs to be transferred between systems.
Advantages of AVRO:
- Efficient Serialization: AVRO’s compact binary format makes it efficient for serialization and deserialization, which is important for performance.
- Schema Evolution: AVRO’s ability to evolve schemas over time without breaking compatibility is one of its most powerful features. This is especially valuable for long-lived datasets.
- Language Independence: Its support for multiple languages makes AVRO a great format for interoperability across different systems and programming environments.
- Small Overhead: The schema is only stored once per file. This means the file size overhead is minimal. This leads to smaller file sizes compared to JSON or XML.







You must be logged in to post a comment.