It is common to deal with JSON files. Often, you’ll need to combine two datasets based on a common key — just like you would with SQL JOINs. In this post, we’ll walk through joining two JSON files and to transform to columns using PySpark, with simple examples you can try immediately.
Here are the steps
- 🛠 Setup: What You Need
- 📂 Sample JSON Files
- 🔥 Step-by-Step Guide
- 🧹 Bonus Tip: Handling Column Name Conflicts
- 📌 Final Notes
🛠 Setup: What You Need
Before we begin, make sure you have:
- Apache Spark installed (or use Databricks, AWS Glue, etc.)
- PySpark available in your environment
If not installed locally, you can do it via pip:
pip install pyspark
📂 Sample JSON Files
Let’s assume we have two JSON files:
File 1: employees.json
[
{"emp_id": 1, "name": "Alice", "dept_id": 101},
{"emp_id": 2, "name": "Bob", "dept_id": 102},
{"emp_id": 3, "name": "Charlie", "dept_id": 101}
]
File 2: departments.json
[
{"dept_id": 101, "dept_name": "HR"},
{"dept_id": 102, "dept_name": "Engineering"},
{"dept_id": 103, "dept_name": "Finance"}
]
We want to join these two files on dept_id.
🔥 Step-by-Step Guide
Initialize Spark Session
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder \
.appName("Join JSON Example") \
.getOrCreate()
Load the JSON Files as DataFrames
# Load employee data
employees_df = spark.read.json("path_to/employees.json")
# Load department data
departments_df = spark.read.json("path_to/departments.json")
You can also inspect the data:
employees_df.show()
departments_df.show()
Perform the Join
Here’s how you can join them using the dept_id column:
# Inner Join: Only matching dept_ids will be kept
joined_df = employees_df.join(departments_df, on="dept_id", how="inner")
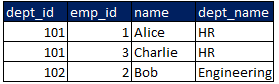
joined_df.show()
✅ Output:
Different Types of Joins
You can also use other join types to transform JSON to columns.
- Left Join: Keep all employees even if no matching department
employees_df.join(departments_df, on="dept_id", how="left").show()
- Right Join: Keep all departments even if no matching employee
employees_df.join(departments_df, on="dept_id", how="right").show()
- Outer Join: Keep everything from both sides
employees_df.join(departments_df, on="dept_id", how="outer").show()
🧹 Bonus Tip: Handling Column Name Conflicts
If the two JSONs have common column names (other than the key), you can rename columns before joining to avoid conflicts:
employees_df.join(departments_df, on="dept_id", how="outer").show()
📌 Final Notes
- Always check the schemas of your JSON files before joining.
- For larger files, consider partitioning and caching your DataFrames for better performance.
- Use broadcast joins if one of the DataFrames is very small, for faster operations.







You must be logged in to post a comment.