Moving data from Amazon S3 into Amazon Redshift is a common task for building analytics pipelines. In this project, we’ll walk through a step-by-step approach to load CSV data from S3 into a Redshift table efficiently and reliably.
🔹 Project Overview
Goal:
- Load raw CSV files from S3 into Redshift.
- Prepare the data for analytics and reporting.
Tech Stack:
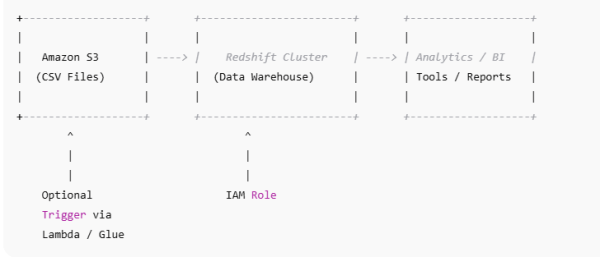
- Amazon S3 → stores raw CSV files.
- Amazon Redshift → analytics data warehouse.
- IAM Role → grants Redshift access to S3.
- SQL COPY command → bulk loads CSV data.
1️⃣ Prepare Your CSV Data in S3
Assume we have sales data in S3:
s3://my-bucket/sales_data/sales_2025_01.csv
s3://my-bucket/sales_data/sales_2025_02.csv
Example CSV content:
order_id,order_date,customer_id,amount
1001,2025-01-01,2001,250.50
1002,2025-01-02,2002,300.00
1003,2025-01-05,2003,150.75
⚠️ Make sure all CSV files have the same schema, otherwise the load may fail.
2️⃣ Create the Redshift Table
Create a table that matches your CSV schema:
CREATE TABLE sales (
order_id INT,
order_date DATE,
customer_id INT,
amount DECIMAL(10,2)
)
DISTKEY(customer_id)
SORTKEY(order_date);
- DISTKEY → optimizes joins on
customer_id. - SORTKEY → improves query performance for
order_datefilters.
3️⃣ Grant Redshift Access to S3
- Create an IAM Role (e.g.,
RedshiftS3ReadRole). - Attach AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess policy.
- Attach the IAM role to your Redshift cluster.
This allows Redshift to securely read files from S3.
4️⃣ Load Data Using COPY
The COPY command efficiently loads data from S3:
COPY sales
FROM 's3://my-bucket/sales_data/'
IAM_ROLE 'arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/RedshiftS3ReadRole'
FORMAT AS CSV
DELIMITER ','
IGNOREHEADER 1
QUOTE AS '"'
REGION 'us-east-1';
Notes:
IGNOREHEADER 1→ skips the header row.DELIMITER ','→ ensures correct CSV parsing.QUOTE AS '"'→ handles quoted fields.- Load multiple files by specifying the S3 folder path.
5️⃣ Validate the Load
Check your data in Redshift:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM sales;
SELECT * FROM sales LIMIT 10;
✅ Optional: For production, also check for duplicates, nulls, or schema mismatches.
6️⃣ Automate the Pipeline
For recurring CSV uploads, consider:
- AWS Glue → ETL jobs to transform and load data.
- AWS Lambda → trigger COPY on S3 file uploads.
- Airflow or Step Functions → orchestrate automated pipelines.
- S3 prefix filtering or manifest files → prevent duplicate loads.
🔹 Key Takeaways
- COPY command is the most efficient way to load large CSVs.
- Use DISTKEY and SORTKEY for query optimization.
- Ensure consistent schema across CSV files.
- Automate using Glue, Lambda, or orchestration tools for production pipelines.
- S3 “partitioning” helps COPY filter files faster but does not partition Redshift storage.
✅ Conclusion
In this project, we built a full S3-to-Redshift pipeline:
- Uploaded CSV files to S3.
- Created a Redshift table with appropriate distribution and sort keys.
- Configured IAM roles for secure access.
- Loaded CSV data efficiently with the COPY command.
- Validated and automated the workflow.
This workflow is production-ready and forms the foundation for scalable data engineering pipelines.







You must be logged in to post a comment.