The CASE statement in SQL is a powerful tool for applying conditional logic directly within your queries. It enables you to handle complex data transformations based on specific criteria without writing lengthy procedural code. In this blog post, we’ll explore five tricky and practical examples that demonstrate how versatile CASE and WHEN can be in real-world SQL scenarios—complete with sample queries and explanations.
- Conditional Aggregation in SQL Using CASE Statements
- Dynamic Value Binning in SQL with CASE and WHEN
- Creating Sequential Numbers in SQL Using CASE
- Handling NULL Values in SQL with CASE Expressions
- Writing Complex Multi-Condition Logic in SQL Using CASE
- Conclusion: Mastering SQL CASE WHEN with Real Examples
Conditional Aggregation in SQL Using CASE Statements
Usage Data
Imagine you have a sales table sales_data1 that records sales amounts and the associated categories.
| id | category | amount |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | 200 |
| 2 | B | 300 |
| 3 | A | 150 |
| 4 | C | 400 |
| 5 | B | 250 |
SQL Query
SELECT category,
Sum(CASE
WHEN amount > 250 THEN amount
ELSE 0
END) AS high_sales
FROM sales_data1
GROUP BY category;
Explanation
This query sums up the amount only for sales greater than 250 and groups the results by category.
Output

Dynamic Value Binning in SQL with CASE and WHEN
Usage Data
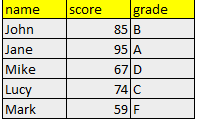
Let’s say we have a students1 table that contains student names and their scores.
| id | name | score |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | 85 |
| 2 | Jane | 95 |
| 3 | Mike | 67 |
| 4 | Lucy | 74 |
| 5 | Mark | 59 |
SQL Query
SELECT
name,
score,
CASE
WHEN score >= 90 THEN 'A'
WHEN score >= 80 THEN 'B'
WHEN score >= 70 THEN 'C'
WHEN score >= 60 THEN 'D'
ELSE 'F'
END AS grade
FROM students1;
Explanation
This query assigns a letter grade based on the student’s score using conditional logic.
Output
Creating Sequential Numbers in SQL Using CASE
Usage Data
Consider a products1 table where you’d like to assign a ranking based on the price.
| id | product_name | price |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Laptop | 1000 |
| 2 | Tablet | 500 |
| 3 | Smartphone | 800 |
| 4 | Desktop | 1200 |
| 5 | Monitor | 300 |
SQL Query
SELECT
product_name,
price,
CASE
WHEN price >= 1000 THEN 'High-End'
WHEN price >= 600 THEN 'Mid-Range'
ELSE 'Budget'
END AS price_category
FROM products1;
Explanation
This query categorizes products into price ranges, allowing for better pricing strategy insights.
Output

Handling NULL Values in SQL with CASE Expressions
Usage Data
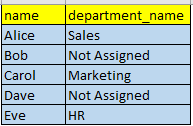
Suppose you have an employees1 table with some missing department data.
| id | name | department |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Alice | Sales |
| 2 | Bob | NULL |
| 3 | Carol | Marketing |
| 4 | Dave | NULL |
| 5 | Eve | HR |
SQL Query
SELECT
name,
CASE
WHEN department IS NULL THEN 'Not Assigned'
ELSE department
END AS department_name
FROM employees1;
Explanation
This query replaces NULL values in the department( column) with the string ‘Not Assigned’.
Output
Writing Complex Multi-Condition Logic in SQL Using CASE
Usage Data
Let’s consider a scenario where we want to apply discounts based on purchase amount in the transactions1 table.
| id | customer_name | purchase_amount |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Charlie | 150 |
| 2 | David | 75 |
| 3 | Emily | 250 |
| 4 | Frank | 450 |
| 5 | Grace | 600 |
SQL Query
SELECT
customer_name,
purchase_amount,
CASE
WHEN purchase_amount >= 500 THEN '20% Discount'
WHEN purchase_amount >= 300 THEN '15% Discount'
WHEN purchase_amount >= 100 THEN '10% Discount'
ELSE 'No Discount'
END AS discount
FROM transactions1;
Explanation
This query assigns discount levels based on the purchase_amount, allowing businesses to target promotions effectively.
Output

Conclusion: Mastering SQL CASE WHEN with Real Examples
The CASE statement in SQL provides a powerful way to include conditional logic directly in your queries. Whether you’re categorizing items, handling nulls, or performing calculations based on various criteria, the versatility of CASE and WHEN can greatly enhance the way you work with data in SQL.
Data to create Tables
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS sales_data1;
CREATE TABLE sales_data1 (
id INT,
category VARCHAR(50),
amount DECIMAL(10, 2)
);
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS students1;
CREATE TABLE students1 (
id INT,
name VARCHAR(50),
score INT
);
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS products1;
CREATE TABLE products1 (
id INT,
product_name VARCHAR(50),
price DECIMAL(10, 2)
);
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS employees1;
CREATE TABLE employees1 (
id INT,
name VARCHAR(50),
department VARCHAR(50)
);
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS transactions1;
CREATE TABLE transactions1 (
id INT,
customer_name VARCHAR(50),
purchase_amount DECIMAL(10, 2)
);
-- Insert data for sales_data1 table
INSERT INTO sales_data1 (id, category, amount) VALUES
(1, 'A', 200),
(2, 'B', 300),
(3, 'A', 150),
(4, 'C', 400),
(5, 'B', 250);
-- Insert data for students1 table
INSERT INTO students1 (id, name, score) VALUES
(1, 'John', 85),
(2, 'Jane', 95),
(3, 'Mike', 67),
(4, 'Lucy', 74),
(5, 'Mark', 59);
-- Insert data for products1 table
INSERT INTO products1 (id, product_name, price) VALUES
(1, 'Laptop', 1000),
(2, 'Tablet', 500),
(3, 'Smartphone', 800),
(4, 'Desktop', 1200),
(5, 'Monitor', 300);
-- Insert data for employees1 table
INSERT INTO employees1 (id, name, department) VALUES
(1, 'Alice', 'Sales'),
(2, 'Bob', NULL),
(3, 'Carol', 'Marketing'),
(4, 'Dave', NULL),
(5, 'Eve', 'HR');
-- Insert data for transactions1 table
INSERT INTO transactions1 (id, customer_name, purchase_amount) VALUES
(1, 'Charlie', 150),
(2, 'David', 75),
(3, 'Emily', 250),
(4, 'Frank', 450),
(5, 'Grace', 600);







You must be logged in to post a comment.